The back, being the most superficial muscle of the upper body, is easier to target. However, to build muscle mass, you have to train your back from multiple angles.
In this article, I’ll show you the 18 best back exercises that help build wider lats, sculpted traps, and a muscular posterior torso.
If want to build a stronger, broader, and proportional back, explore these exercises and include them in your workout muscle-building program.
The Back Muscles
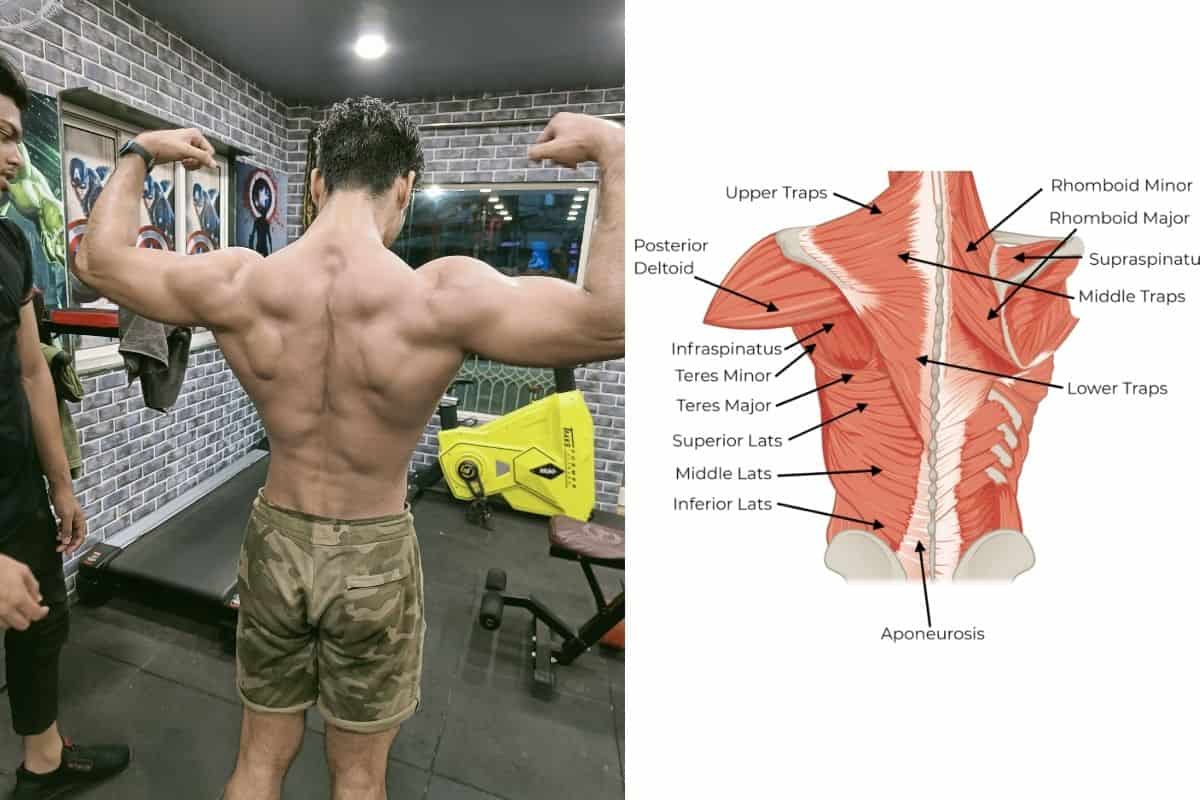
To build a strong back, you need to target all muscles of the back, such as;
- Trapezius ( Upper, middle, and lower traps)
- The Rhomboids major and minor (which are structured beneath the trapezius muscle)
- Latissimus dorsi or Lats (Superior, middle and inferior)
- Infraspinatus (this is one of the rotator cuff muscles)
- The last but important one is the erector spinae or the lower back.
I’ll share exercises for each of these muscles so you can train your back from all angles and build a thick, wider, and symmetrical back.
18 Best Bodybuilding Back Exercises for Maximum Mass Gain
Here are all the best back exercises for mass and strength development. The first ten exercises will be compound movements, and the rest will be isolation exercises. Combining them will help you develop a superior back over time.
- Pull-ups
- Deadlift
- Bent Over Barbell Row
- Dumbbell IYT Raises
- Inverted Row
- Barbell T Rowing
- Dumbbell Pullover
- Lat Pulldown
- Seated Cable Row
- Single Arm Dumbbell Rowing
- V Grip Lat Pulldown
- Facepull
- TRX row
- Chin-ups
- Standing Cable Lat Pullover
- Kettlebell Bent Over Row
- Pendlay Row
- Seal Row
Below is the step-by-step guide on how to do each back workout.
1. Pull-Ups

The pull-up is the best bodyweight exercise that stimulates several muscles simultaneously, such as; the lats, rhomboids, traps, and deltoids, and builds a stronger and wider back.1 Ronai, Peter MS, RCEP, CSCSD, NSCA-CPTD; Scibek, Eric MS, ATC, CSCS. The Pull-up. Strength and Conditioning Journal 36(3):p 88-90, June 2014. | DOI: 10.1519/SSC.0000000000000052, 2Snarr RL, Hallmark AV, Casey JC, Esco MR. Electromyographical Comparison of a Traditional, Suspension Device, and Towel Pull-Up. J Hum Kinet. 2017;58:5-13. Published 2017 Aug 1. doi:10.1515/hukin-2017-0068
It is one of my favorite back exercises. I often do it with and without weight to increase my pulling strength and build wider lats.
How to do it:
- Start with standing under the center of a pull-up bar.
- Reach onto a pull-up bar and grip with your hands 1.5x wider than shoulder-width, palms facing down and away.
- Keep your arms extended and your knees slightly bent. That’s the starting position.
- Brace your core and pull your body up until your chin is just above the bar, and then slowly lower your body in a controlled way while ensuring you feel muscle activation as you pull.
- Pause for a moment and then return to the beginning. That’s one complete rep.
You can do as many reps as possible.
Other instructions:
- You can also keep your legs crossed instead of keeping them straight.
- Your chest should be up while lifting as it produces maximum contraction in the back.3 The Perfect Pull-Up – Do it Right! – Calisthenicmovement
- Do not flare your elbows out because it may reduce the effectiveness of pull-ups.
2. Deadlift

The deadlift is the king of all lifts as it engages multiple muscles from the upper to the lower body, including the latissimus dorsi (lats) and lower back.4 Holmes, Clifton. (2019). Understanding the deadlift and its variations. ACSMʼs Health & Fitness Journal. 24. 10.1249/FIT.0000000000000570.
Mr. Olympia champions, like Ronnie Coleman, Jay Cutler, Dorian Yates, and Arnold, frequently perform deadlifts on their pull day to develop strength and build a strong physique, particularly the back.
How to do the deadlift:
- Place a bar on the floor before you and put appropriate weight into it.
- Stand upright (shoulder-width stance) with your shin close to the bar.
- Push your hips backward, bend your knees, and grab the bar firmly with an alternate grip, maintaining a flat back.
- Brace your core, inhale deeply, and lift the bar with full strength until your hips are fully extended.
- Hold for a couple of seconds, then slowly lower the weights on the floor.
Other instructions:
- Wear a gym belt as it provides stability to your lower back during the lift.
- Push your heels into the floor to generate strength to lift the bar effectively.
- Raise your shoulder blades together as you lift the weight from the ground.
- Your hips will come forward when you fully extend your knees.
- Keep your back as flat as possible during the entire movement.
- Perform each rep slowly by engaging your lats to get the best out of each repetition.
If you work out at home with dumbbells, you can do various dumbbell deadlifts.
3. Bent Over Row

The bent-over row is a compound workout that works on numerous muscles simultaneously, such as the deltoids, arms, and especially the back.
It hits the middle traps, lats, rhomboids, and infraspinatus and stimulates muscle growth.5 Fenwick CM, Brown SH, McGill SM. Comparison of different rowing exercises: trunk muscle activation and lumbar spine motion, load, and stiffness. J Strength Cond Res. 2009 Mar;23(2):350-8. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181942019. PMID: 19197209, 6Saeterbakken A, Andersen V, Brudeseth A, Lund H, Fimland MS. The Effect of Performing Bi- and Unilateral Row Exercises on Core Muscle Activation. Int J Sports Med. 2015 Nov;36(11):900-5. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1398646. Epub 2015 Jul 2. PMID: 26134664, 7What Is the Best Back Exercise? by Holly Edelburg, B.S., John P. Porcari, Ph.D., Clayton Camic, Ph.D., Attila Kovacs, Ph.D., and Carl Foster, Ph.D., with Daniel J. Green – American Council of Exercise (ACE) Research
If you want to smoke back gains while building strength and stability, you should incorporate this exercise into your hypertrophy workout routine.
How to do it:
- Stand with your feet hip-width apart, holding a bar with your hands with an overhand grip. Palms facing down.
- Slightly bend your knees, lean forward while maintaining a flat back, and keep your core tight. That’s the starting position.
- Now raise the bar toward your stomach until you feel the full contraction in the back muscles.
- Hold for a second at the top, then slowly lower to the starting position. That’s one rep.
Other instructions:
- The suggested repetitions for this exercise are at least 6-10 in each set.
- Keep your chest up and remain bent during the whole movement.
4. I Y T Raises
The IYT raises is a unique and effective multi-movement exercise that targets the shoulder and back simultaneously and helps develop a firm torso.
It mostly engages the trapezius and infraspinatus and helps improve back muscle definition. (7)
You need a pair of dumbbells and an adjustable bench to perform this movement. The steps are below:
- Lie on your stomach on a 30-degree incline bench, holding a dumbbell in each hand with a neutral or overhand grip.
- Keep your chest at the corner of a bench with your arms extended underneath.
- Now to form the letter “I,” raise the dumbbells forward in front of you until they are parallel to the floor. Hold for a second and then slowly lower them back to the starting position.
- To form the letter “Y,” raise the dumbbells upward at a 45-degree angle so that your body forms a “Y” shape. Hold for a moment and then slowly return to the initial position. Make sure you squeeze your shoulder blades together at the top.
- To form the letter T, raise the dumbbells out to the sides until they are parallel to the ground. Make sure your body looks in the “T” shape at the top. Hold for a second and then slowly return to the beginning position. That’s one complete rep.
Other instructions:
- Use light dumbbells (4-8 lbs) or even just your body weight if you’re a beginner. The focus is on form and control, not heavy lifting.
- Keep your arms straight to ensure the focus stays on your back.
5. Inverted Row
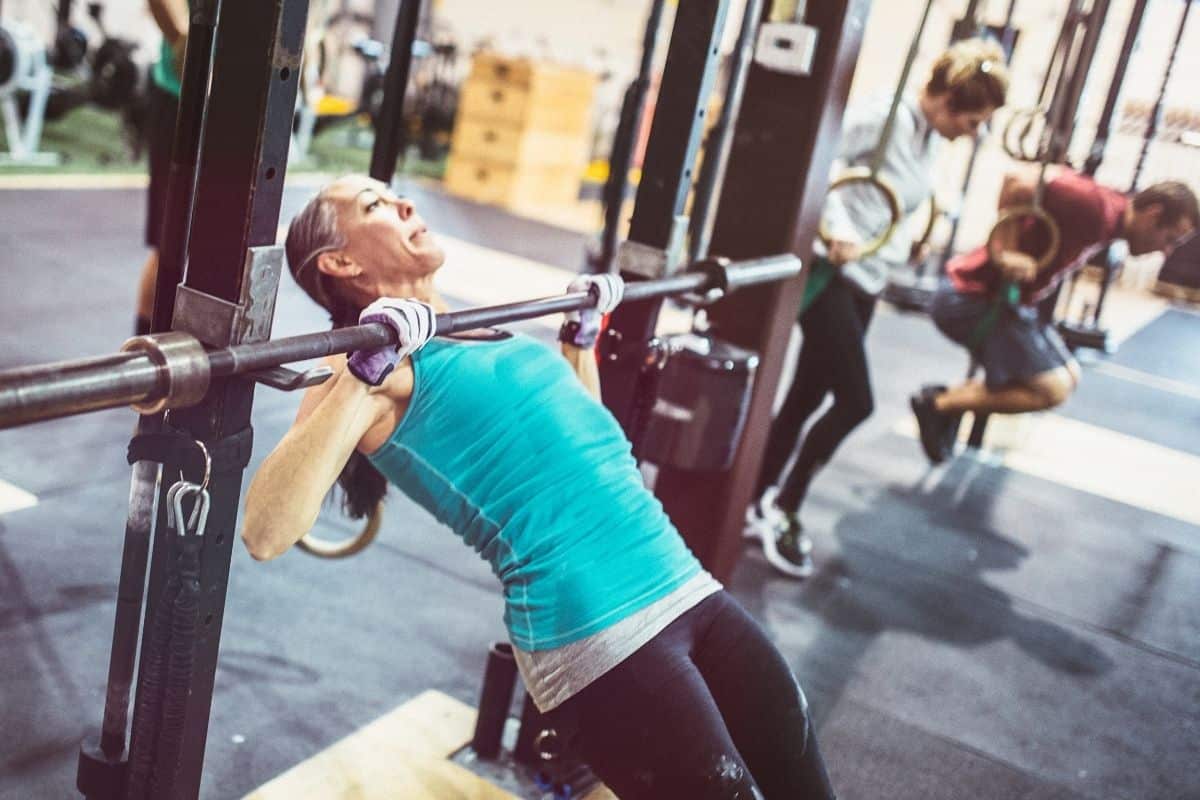

The inverted row is an easy but effective exercise for upper-body muscular development. It is a bodyweight exercise, requiring you to get under the bar and pull yourself up.8 Snarr, Ronald & Esco, Michael. (2013). Exercise Highlight: Inverted Row. Journal of Australian Strength and Conditioning. 21.
It primarily activates the trapezius and lats and helps develop a well-rounded back.9 Youdas JW, Keith JM, Nonn DE, Squires AC, Hollman JH. Activation of Spinal Stabilizers and Shoulder Complex Muscles During an Inverted Row Using a Portable Pull-up Device and Body Weight Resistance. J Strength Cond Res. 2016 Jul;30(7):1933-41. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000001210. PMID: 26422610.
You can do it under a desk or the Smith machine. The best and safest way to do it is by using the Smith machine.
Here are the steps:
- Set up the bar in the Smith machine and lay it on your back underneath. Now reach onto the bar to grab with your hands with an overhand grip. Make sure your hands are shoulder-width apart.
- Now brace your core and pull your torso toward the bar until your chest reaches the bar. And then slowly lower your body in a controlled way while ensuring you feel muscle activation as you pull and return to the beginning.
- That will be one complete rep. You can do as many as you can.
Other instructions:
- Squeeze your shoulder blades together at the top.
- Avoid rounding your back during the movement.
- Keep your body straight from head to heels.
- Inhale before pulling the bar and exhale before returning to the start.
Doing an inverted row will help you improve your pulling strength and allow you to do more pull-ups. If you’re not good at doing pull-ups, do more inverted rows.
Other Inverted Row Variations:
- Modified Inverted Row
- Single-arm Inverted Row
- Suspended Inverted Row
6. Barbell T Rowing

The barbell T row enables you to lift heavy weights and allows you to hit your back with a prone and neutral grip. The different grip and heavy weight will help you in building mid-back thickness and lat width.
It has a limited range of motion than the standard bent-over row but studies suggest that a partial range of motion is also effective for stimulating muscle hypertrophy.10 Goto M, Maeda C, Hirayama T, Terada S, Nirengi S, Kurosawa Y, Nagano A, Hamaoka T. Partial Range of Motion Exercise Is Effective for Facilitating Muscle Hypertrophy and Function Through Sustained Intramuscular Hypoxia in Young Trained Men. J Strength Cond Res. 2019 May;33(5):1286-1294. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000002051. PMID: 31034463.
How to do it:
- Get an empty barbell and place one end against the wall.
- Put appropriate weight into another end of the bar.
- Stand over it in a shoulder-width stance so the bar is in between your feet.
- Place the v-handle under the bar for lifting the weights.
- Hinge at your hips and bend your torso forward so the weights are underneath your chest.
- Grab the handle firmly with a neutral grip and keep your arms straight. This was the setup.
- Pulling the weights up, bring your elbows behind until your back muscles are fully engaged.
- Hold for a couple of seconds and then lower the weights on the floor in a controlled fashion.
Other instructions:
- Before you lift, puff your chest out and pull your shoulder blades together slightly. This pre-engages your back muscles and protects your spine.
- Before you lift, puff your chest out and pull your shoulder blades together slightly. This pre-engages your back muscles and protects your spine.
- Use a neutral grip (palms facing each other) to reduce strain on your wrists and increase lat activation, as well as a shoulder-width prone grip to hit the upper back more.
7. Dumbbell Lat Pullover
The dumbbell pullover is an excellent exercise for muscle building. It works on the pecs and lats and helps build a solid trunk.
It involves lying on a bench and extending your arms behind your head, allowing your lats to stretch and contract throughout the movement.
You can do it in a couple of ways, such as lying vertically or horizontally on the bench.
Let’s find out how to perform a dumbbell pullover to stimulate back muscles effectively:
- Grab the head of a dumbbell with your hands.
- Place your upper back on a flat bench and keep your feet flat on the ground.
- Extend your arms behind your head with a slight bend in your elbows. Your palms should be facing upward.
- Brace your abdominal muscles and pull the weight over you until you feel the full contraction.
- Hold for a few seconds, then slowly return your arms behind your head.
Other Instructions:
- Drop the hips slightly lower than the bench allows for a greater stretch to be placed directly on the lats.11 How To Do A Dumbbell Pullover By Jeff Cavaliere MSPT, CSCS – Athleanx.com
- Keep your shoulder blades pinched together throughout the movement
8. Lat Pulldown

The lat pulldown engages the entire back muscles, primarily the latissimus dorsi. It increases pulling strength, improves posture, and plays a key role in developing a bigger and broader back.12 Snarr, Ronald & Abbott, Patricia. (2015). A Comparative Analysis and Technique of the Lat Pull-down. Strength and Conditioning Journal. 37. 21-25. 10.1519/SSC.0000000000000173
Research has also shown lat pulldown helps improve pull-up performance. So if you struggle to lift yourself toward the pull-up bar but you want to do that, the pulldown should be one of your primary lifts.13 Li Q, Yan J, Dai H, Qiao M, Gong M, Niu W, Yang Y, Wang L. Effect of Eight-Week Transcranial Direct-Current Stimulation Combined with Lat Pull-Down Resistance Training on Improving Pull-Up Performance for Male College Students. Life. 2025; 15(1):128. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15010128
How to do it:
- Sit on the bench below the center of a pull-down bar and adjust your leg.
- Grab the bar with your hands slightly wider than shoulder-width apart.14 Andersen V, Fimland MS, Wiik E, Skoglund A, Saeterbakken AH. Effects of grip width on muscle strength and activation in the lat pull-down. J Strength Cond Res. 2014 Apr;28(4):1135-42. doi: 10.1097/JSC.0000000000000232. PMID: 24662157
- Brace your core and slightly lean your torso back so that it comes toward the chest when you pull the bar down.
- Pull the bar toward your chest until you feel the full contraction in the lats.
- Return to the start by extending your elbows. That’s one rep.
Perform the lat pulldown twice a week for a better result.
Other instructions:
- Avoid rounding your back during the movement.
- Inhale before pulling the bar.
- Pause for a moment at the bottom of the lift and do it in a controlled way.
Other variations of the lat pulldown exercise:
- Behind-The-Neck Lat Pull-Down
- V-Bar or D-Handles Pull-Down
- Reverse Close-Grip Lat Pull-Down
- Single-Arm Lat Pull-Down
Front Vs. Rear Pull-Downs
- According to several studies published in the Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, lat pulldown exercise with a wide grip where the bar comes in front of your neck produced greater muscle activity in the lats than wide-grip lat pulldown where the bar comes behind the neck.15 Sperandei S, Barros MA, Silveira-Júnior PC, Oliveira CG. Electromyographic analysis of three different types of lat pull-down. J Strength Cond Res. 2009 Oct;23(7):2033-8. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181b8d30a. PMID: 19855327.
- Behind-the-neck pulldown puts more stress on the rotator cuff, which sometimes becomes harder to stabilize the shoulder joints, which causes injuries or soreness.
9. Seated Cable Row
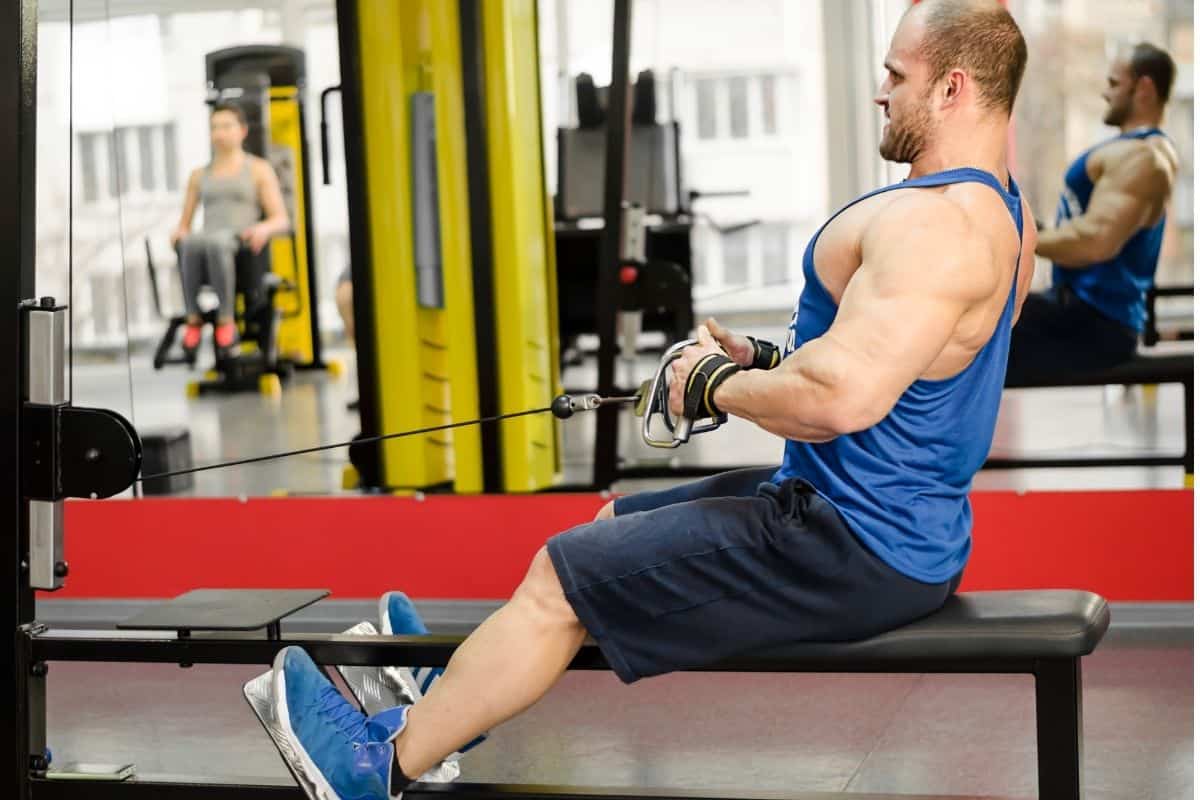

The seated cable row is another excellent back exercise for muscle development. It builds a stronger back by targeting the lats, rhomboids, and traps.
It also promotes spinal alignment and improves posture and upper body functionality, including in older people.16 Balachandran, A., Martins, M. M., De Faveri, F. G., Alan, O., Cetinkaya, F., & Signorile, J. F. (2016). Functional strength training: Seated machine vs standing cable training to improve physical function in the elderly. Experimental Gerontology, 82, 131-138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2016.06.012
This exercise requires a cable pulley or rowing machine which is easily accessible in almost all gyms, whether large or small. So, make sure to utilize a seated row as much as possible to build a thicker back.
How to do it:
- Set the desired weight on the weight stack and attach the D-handle to the hook.
- Sit on the machine’s bench, extend your arms, and grab the handles with a neutral grip, palms facing each other.
- Keep your back straight, chest up, and legs slightly bent, or keep your feet on the pad if available.
- Now pull the handles toward your stomach until it reaches close to your body.
- Pause for a moment, feel the full contraction, and return to the start.
Other Instructions:
- You can use variations of close grip, prone grip, and medium grip to emphasize different muscles.
- Drive your elbows toward your side and focus on contracting your lats.
10. Single-arm DB Rowing

The one-arm dumbbell row is a unilateral exercise that helps target each side of the back muscle individually and helps improve strength and muscle imbalance.
It allows your shoulder and elbow to move more freely, letting you stretch and contract your lats (latissimus dorsi) more thoroughly and build a defined back.
The unilateral row is also easier on the spine than bent-over barbell rows, making it suitable for newbies.
How to do it:
- Grab a dumbbell in your right hand with a neutral grip.
- Place your left knee on one end of a flat bench and your right foot firmly on the floor.
- Put your left hand on the bench with your arms straight underneath your shoulder.
- Let your right arm hang straight below your shoulder. That’s the start.
- Keep your core tight, and driving your elbows up pull the dumbbell at your side.
- Return to the start, perform the desired reps, and repeat on the opposite side.
Other Instructions:
- Keep your back straight and avoid twisting your torso. You should focus on isolating your back muscles, not swing the weight with momentum.
- Imagine driving your elbow back toward your hip, not just lifting the dumbbell with your hand. This cues your lats and mid-back to do the work instead of your biceps.
- Lower the weight slowly (2-3 seconds) to increase time under tension. This eccentric phase is where a lot of muscle growth happens.
- Let the dumbbell pull your shoulder down at the bottom of the movement (without yanking your arm out of the socket). This stretch enhances flexibility and strengthens the core.17 Saeterbakken A, Andersen V, Brudeseth A, Lund H, Fimland MS. The Effect of Performing Bi- and Unilateral Row Exercises on Core Muscle Activation. Int J Sports Med. 2015 Nov;36(11):900-5. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1398646. Epub 2015 Jul 2. PMID: 26134664.
11. V Handle Lat Pulldown
Doing lat pull-downs with a V handle yields better results than behind-the-neck pulldowns. It targets the traps and lats effectively and helps improve muscle definition.
It also engages the biceps and enhances pulling strength.18 The Biomechanics of the Lat Pulldown: Muscles Worked, Grips, & Form – National Academy of Sports Medicine (NASM)
How to do V grip Lat pulldown
- Anchor the attachment handle in the lat pulldown machine and sit underneath it.
- Grab the handle firmly with a neutral grip.
- Slightly lean back and pull the handle down toward your chest until your back muscles are fully engaged.
- Hold for a couple of seconds and return to the starting point. That’s one rep.
Do three to four sets of six to ten reps each with 2 to 3 minutes of rest between sets.
Other Instructions:
- Experiment with a 3-1-2 tempo (3 seconds down, 1-second pause, 2 seconds up) to increase time under tension.
- Switch between neutral and pronated grips every few weeks to target slightly different muscle fibers and avoid adaptation.
12. Face Pull
The face pull targets the rear delt, rhomboids, and traps and improves the look of your back.19 Yoo WG. Effects of pulling direction on the upper trapezius and rhomboid muscle activity. J Phys Ther Sci. 2017 Jun;29(6):1043-1044. doi: 10.1589/jpts.29.1043. Epub 2017 Jun 7. PMID: 28626320; PMCID: PMC5468195
If you train at the gym, incorporate face pull either on shoulder day or the back day.
How to do face pulls:
- Set the rope at a suitable height and firmly grab it with your hands.
- Step back a few inches until you stand in an appropriate position where your arms can extend fully in front of you.
- Stand in the shoulder-width stance and slightly lean back, but keep your back straight. This is your starting position.
- Pull the rope towards your face so the upper back muscles can engage.
- Hold for a couple of seconds, and then extend your arms fully in front of you. That’s one repetition.
Other Instructions:
- Set the cable pulley at or slightly above face level. A higher anchor point shifts more emphasis to the upper traps and rhomboids compared to a lower setting.
- Focus on pulling your shoulder blades together (retraction) as you draw the rope toward your face. Think “pinch the spine” rather than just pulling with your arms.
13. TRX row
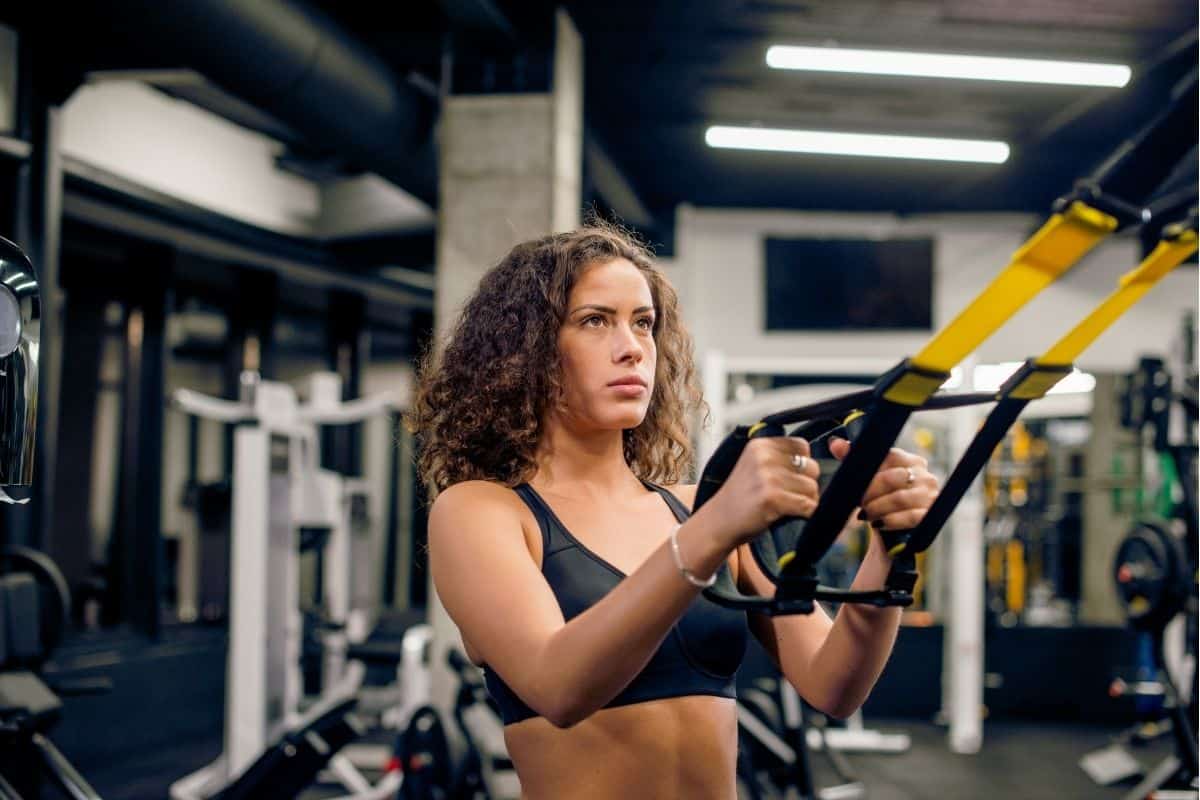

In terms of muscle activation, TRX row wouldn’t be a good option among these exercises. However, it works on the major muscles of the back, such as the upper and middle traps, latissimus dorsi, and the rhomboid.
It also provides other benefits which are essential for overall fitness, including body balance and stability.
How to do the TRX Rows:
- Stand with your feet, holding a TRX handle in each hand with a neutral grip, palms facing others. Keep the hip-width distance between your feet.
- Take one step forward with your right foot while keeping the other in the same position and both feet facing forward.
- Pull your shoulder blades down and back so that you can lean backward.
- Keep your body straight in line, and your body weight shifted over the back of your legs when you straighten the elbows. Your elbows should be at chest height.
- Now brace your core, bend the elbows at your sides, and pull your chest toward your hands.
- Hold for a second, then extend your arms to lower your body back to the beginning. That’s one rep.
Other Instructions:
- Start at a 45-degree angle and progress toward parallel to the ground as strength improves.
- Initiate the pull by squeezing your shoulder blades together (retraction) before bending your elbows. Hold the squeeze at the top for 1–2 seconds to maximize rhomboid and trap activation.
- Lower yourself slowly to increase time under tension (TUT) and pull explosively but controlled to recruit fast-twitch fibers in the lats and traps.20 Burd NA, Andrews RJ, West DW, et al. Muscle time under tension during resistance exercise stimulates differential muscle protein sub-fractional synthetic responses in men. J Physiol. 2012;590(2):351-362. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2011.221200
14. Chin-ups
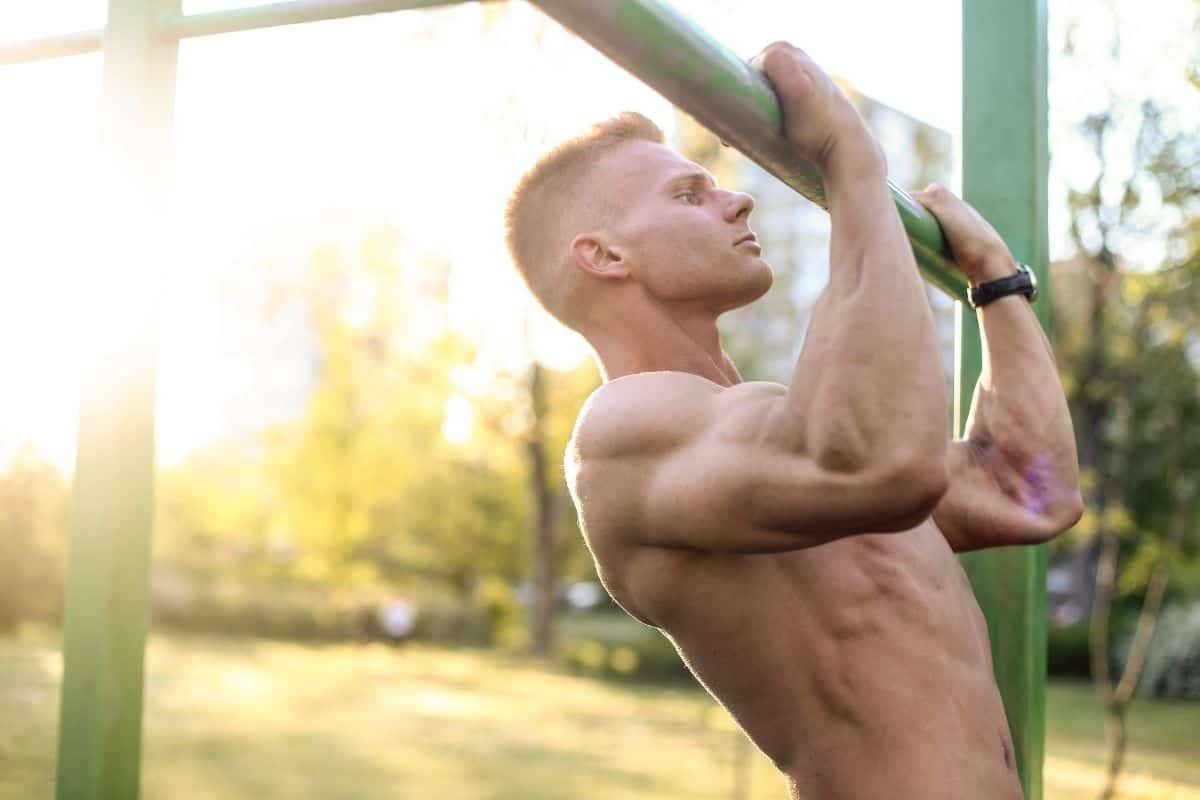

A chin-up is a compound movement that simultaneously strengthens your biceps and back. For the back, it heavily activates the lats (the large back muscles) and helps increase back width and shape.21 ACE Technique Series: Chin-ups by Pete McCall, Health and Fitness Expert (American Council of Exercise), 22Youdas JW, Amundson CL, Cicero KS, Hahn JJ, Harezlak DT, Hollman JH. Surface electromyographic activation patterns and elbow joint motion during a pull-up, chin-up, or perfect-pullup™ rotational exercise. J Strength Cond Res. 2010 Dec;24(12):3404-14. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181f1598c. PMID: 21068680, 23Doma K, Deakin GB, Ness KF. Kinematic and electromyographic comparisons between chin-ups and Lat pull-down exercises. Sports Biomech. 2013 Sep;12(3):302-13. doi: 10.1080/14763141.2012.760204. PMID: 24245055
How to do a chin-up
- Grab the bar with an underhand grip and hang onto it with your hands hip-width apart.
- Brace your core, bend your knees, and pull yourself upward until your chin is close to the bar.
- Hold a moment at the top (you’ll feel the contraction in your back muscles), and then lower your body until your arms are straight.
Other Instructions:
- Hang fully at the bottom (arms extended) to stretch the lats, then pull your chest toward the bar, leading with your elbows. Avoid swinging or kipping. Keep it strict to target the back.
- Use a shoulder-width supinated grip (palms facing you) to emphasize lats and biceps. Slightly wider grips shift more focus to the lats.
- Experiment with neutral-grip pull-ups (palms facing each other) later to hit the back from different angles.
- Push to muscle failure (can’t do another clean rep) within your rep range to trigger growth, but stop if form breaks down.
15. Standing Rope Pulldown
Standing pull-down, also known as straight arm cable pullover, is a good variation to hit the lats from a different technique.
It involves standing in a slightly leaning position and pulling the cable with straight arms, keeping your elbows close to the body.
This exercise isolates the lats through a long range of motion and enhances width and definition.24 Cable pullovers for lats – r/naturalbodybuilding – Reddit.com
The cable pullover also strengthens abdominal muscles and builds pulling power.
Let’s find out how to do a standing pulldown with a rope:
- Set the rope at the highest point of the cable machine and firmly grab it with your hands.
- Stand in the staggered or normal shoulder-width stance.
- Keeping your back straight and core tight, pull the rope towards you. Your chest will be up and forward when you pull the rope.
- Pause for a few seconds to feel the contraction in your back and then return your arms to the starting position. This is your one repetition.
Other Instructions:
- Focus on squeezing your lats at the bottom of the pull, not just moving the weight. Imagine pulling your shoulder blades down and back.
- Keep a slight bend in your knees and avoid rounding your back. A stable base amplifies lat activation.
16. Kettlebell Bent-over Row
If you’re someone who works out with kettlebells at home, you can incorporate Gorilla rows in your regime to build a stronger back.
You can also use it to improve muscle imbalance and back definition as it involves training one side at a time.
Ho to do bent-over row with kettlebells
- Grab a pair of kettlebells with a neutral grip and stand in a slightly wider than shoulder-width stance.
- Hinge at your hips and lean your torso forward until your chest is parallel to the ground.
- Let your arms hang straight below your chest with palms facing each other.
- Keeping your back straight and core tight, pull the weights towards you until your lat muscle is engaged.
- Hold for a couple of seconds at the top, and then lower your arms to the start. This is your one repetition.
Other Instructions:
- Keep your back flat and chest up and avoid rounding your spine to efficiently target the lats.
- If one side lags, do an extra rep or two to balance it out.
17. Pendlay Row
Pendlay row is a high-intense barbell exercise that fires up muscles around the back and shoulder and builds up a firm torso while improving explosive strength.
Steps to perform Pendlay Rows:
- Put the desired plates into the barbell, grab it firmly with an overhand grip, and stand in a shoulder-width stance.
- Bend your torso until your chest is parallel to the ground. Core tight, chest up, and knees slightly bent.
- Driving your elbows, pull the bar until it touches your stomach, then lower the bar down till it touches the floor. Repeat.
Other Instructions:
- Lower the bar in 1-2 seconds to feel the tension in the back.
- Brace the core, glutes, and thigh to stay firmly and row the bar effectively.
18. SEAL Row
The SEAL row hits the upper back, including the traps and posterior delt, and helps forge a solid back.
It has a greater range of motion, providing decent stretch to the lats and traps, and helps build a strong back and upright posture.
The Seal row involves the following steps:
- Place the ends of a flat bench on the steppers, grab one dumbbell in each hand, and lie prone on the bench with your face facing down.
- Row the dumbbells at your sides until your back muscles are fully engaged.
Other Instructions:
- Row the dumbbells or bar to touch the underside of the bench (mid-to-upper abs level), driving elbows back. This ensures max lat and mid-back contraction.
Tips to Optimize Back Workout for Maximum Gains
If you want to beef up your back muscles, you need to incorporate heavy compound lifts and isolation workouts in your gym workout routine for your back.
Compound lifts help you target the entire back muscles at once, such as the lats, traps, lower back, erector spinae, and rotator cuff.
Deadlifts, pull-ups, barbell bent-over rows, IYT raises, inverted rows, and barbell T rowing are some of the best compound lift workouts that will help you build mass and strength.
After the compound exercises, you’ll need to do isolation workouts that help you target your specific back muscles at a time.
Lat pulldown, seated rowing, TRX row, chin-ups, reverse fly, pullover, and face pull are some of the best isolation back workouts you can do at the gym to build muscle mass.
Once you select the best exercises for your back, you’ll need to perform them in the correct form.
Doing exercises with the proper form and technique yields better results and promotes strength and hypertrophy
1. Grip
Use “Thumbless Grip.” It means to keep your thumbs over the bar or dumbbells instead of underneath.
Keeping the thumbs over the bar elicits higher muscle activation and engages working muscles effectively.
Whether you pull down or pullups, try using a thumbless grip because it works well during back workouts.
2. Use “Elbows” instead of “Hands” at the time of rowing
Use your elbows instead of your hands at the rowing or pulling. Because using elbows activates more back muscles and reduces wrist involvement.
Doing this not only activates muscles intensely but also helps you do more reps and sets.
3. Keep your shoulders down and away from the head
Keeping the shoulder down and away from the neck puts less stress on the traps, helps you perform back exercises with ease, and enables you to do more repetitions and build wider lats.
Weekly Back Workout Routine for Strength and Mass
If you want to develop your back muscles, I suggest you do back exercises twice a week.
Doing back workouts two times a week will help you increase strength and mass over time.
Here is the back workout routine you can do at the gym to build a superior back
Week 1 – Day 1
- Pullup – As many reps as possible x 3 sets
- Deadlift – 8, 6, 4, 4 reps
- Standard Lat Pulldown – 12, 10, 8, 6
- Seated Rowing – 12, 10, 8, 6
- Single-arm DB Rowing – 10, 8, 6
- Facepull – 10, 8, 6
Week 1 – Day 2
- Pull-Ups – As many reps as possible x 3 sets
- Standing Pulldown – 12, 10, 8
- V Handle Pulldown – 12, 10, 8
- Bent Over Row – 12, 10, 8, 6
- Seated Rowing – 12, 10, 8
- Barbell T Rowing – 12, 10, 8, 6
You can change or replace an exercise from this routine, depending on your fitness level.
Download The Back Workout and Exercises PDF
Download the best back exercises PDF that can help you boost strength, beef up muscles, and build a wider and bigger back.
References
- 1Ronai, Peter MS, RCEP, CSCSD, NSCA-CPTD; Scibek, Eric MS, ATC, CSCS. The Pull-up. Strength and Conditioning Journal 36(3):p 88-90, June 2014. | DOI: 10.1519/SSC.0000000000000052
- 2Snarr RL, Hallmark AV, Casey JC, Esco MR. Electromyographical Comparison of a Traditional, Suspension Device, and Towel Pull-Up. J Hum Kinet. 2017;58:5-13. Published 2017 Aug 1. doi:10.1515/hukin-2017-0068
- 3The Perfect Pull-Up – Do it Right! – Calisthenicmovement
- 4Holmes, Clifton. (2019). Understanding the deadlift and its variations. ACSMʼs Health & Fitness Journal. 24. 10.1249/FIT.0000000000000570.
- 5Fenwick CM, Brown SH, McGill SM. Comparison of different rowing exercises: trunk muscle activation and lumbar spine motion, load, and stiffness. J Strength Cond Res. 2009 Mar;23(2):350-8. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181942019. PMID: 19197209
- 6Saeterbakken A, Andersen V, Brudeseth A, Lund H, Fimland MS. The Effect of Performing Bi- and Unilateral Row Exercises on Core Muscle Activation. Int J Sports Med. 2015 Nov;36(11):900-5. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1398646. Epub 2015 Jul 2. PMID: 26134664
- 7What Is the Best Back Exercise? by Holly Edelburg, B.S., John P. Porcari, Ph.D., Clayton Camic, Ph.D., Attila Kovacs, Ph.D., and Carl Foster, Ph.D., with Daniel J. Green – American Council of Exercise (ACE) Research
- 8Snarr, Ronald & Esco, Michael. (2013). Exercise Highlight: Inverted Row. Journal of Australian Strength and Conditioning. 21.
- 9Youdas JW, Keith JM, Nonn DE, Squires AC, Hollman JH. Activation of Spinal Stabilizers and Shoulder Complex Muscles During an Inverted Row Using a Portable Pull-up Device and Body Weight Resistance. J Strength Cond Res. 2016 Jul;30(7):1933-41. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000001210. PMID: 26422610.
- 10Goto M, Maeda C, Hirayama T, Terada S, Nirengi S, Kurosawa Y, Nagano A, Hamaoka T. Partial Range of Motion Exercise Is Effective for Facilitating Muscle Hypertrophy and Function Through Sustained Intramuscular Hypoxia in Young Trained Men. J Strength Cond Res. 2019 May;33(5):1286-1294. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000002051. PMID: 31034463.
- 11How To Do A Dumbbell Pullover By Jeff Cavaliere MSPT, CSCS – Athleanx.com
- 12Snarr, Ronald & Abbott, Patricia. (2015). A Comparative Analysis and Technique of the Lat Pull-down. Strength and Conditioning Journal. 37. 21-25. 10.1519/SSC.0000000000000173
- 13Li Q, Yan J, Dai H, Qiao M, Gong M, Niu W, Yang Y, Wang L. Effect of Eight-Week Transcranial Direct-Current Stimulation Combined with Lat Pull-Down Resistance Training on Improving Pull-Up Performance for Male College Students. Life. 2025; 15(1):128. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15010128
- 14Andersen V, Fimland MS, Wiik E, Skoglund A, Saeterbakken AH. Effects of grip width on muscle strength and activation in the lat pull-down. J Strength Cond Res. 2014 Apr;28(4):1135-42. doi: 10.1097/JSC.0000000000000232. PMID: 24662157
- 15Sperandei S, Barros MA, Silveira-Júnior PC, Oliveira CG. Electromyographic analysis of three different types of lat pull-down. J Strength Cond Res. 2009 Oct;23(7):2033-8. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181b8d30a. PMID: 19855327.
- 16Balachandran, A., Martins, M. M., De Faveri, F. G., Alan, O., Cetinkaya, F., & Signorile, J. F. (2016). Functional strength training: Seated machine vs standing cable training to improve physical function in the elderly. Experimental Gerontology, 82, 131-138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2016.06.012
- 17Saeterbakken A, Andersen V, Brudeseth A, Lund H, Fimland MS. The Effect of Performing Bi- and Unilateral Row Exercises on Core Muscle Activation. Int J Sports Med. 2015 Nov;36(11):900-5. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1398646. Epub 2015 Jul 2. PMID: 26134664.
- 18The Biomechanics of the Lat Pulldown: Muscles Worked, Grips, & Form – National Academy of Sports Medicine (NASM)
- 19Yoo WG. Effects of pulling direction on the upper trapezius and rhomboid muscle activity. J Phys Ther Sci. 2017 Jun;29(6):1043-1044. doi: 10.1589/jpts.29.1043. Epub 2017 Jun 7. PMID: 28626320; PMCID: PMC5468195
- 20Burd NA, Andrews RJ, West DW, et al. Muscle time under tension during resistance exercise stimulates differential muscle protein sub-fractional synthetic responses in men. J Physiol. 2012;590(2):351-362. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2011.221200
- 21ACE Technique Series: Chin-ups by Pete McCall, Health and Fitness Expert (American Council of Exercise)
- 22Youdas JW, Amundson CL, Cicero KS, Hahn JJ, Harezlak DT, Hollman JH. Surface electromyographic activation patterns and elbow joint motion during a pull-up, chin-up, or perfect-pullup™ rotational exercise. J Strength Cond Res. 2010 Dec;24(12):3404-14. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181f1598c. PMID: 21068680
- 23Doma K, Deakin GB, Ness KF. Kinematic and electromyographic comparisons between chin-ups and Lat pull-down exercises. Sports Biomech. 2013 Sep;12(3):302-13. doi: 10.1080/14763141.2012.760204. PMID: 24245055
- 24Cable pullovers for lats – r/naturalbodybuilding – Reddit.com






